The IT Essentials Final Exam 1-14 looms on the horizon, promising both a challenge and an opportunity for IT enthusiasts. Prepare to conquer this pivotal assessment with our comprehensive guide, designed to empower you with knowledge and confidence.
Our expert team has meticulously crafted this guide, covering every nook and cranny of the exam. From networking fundamentals to cloud computing, you’ll find all the essential concepts laid out in an engaging and accessible manner.
Exam Overview
The IT Essentials final exam 1-14 is a comprehensive assessment of your knowledge and skills in the field of IT. The exam consists of 75 multiple-choice questions and has a time limit of 90 minutes. The exam is graded on a scale of 1000 points, with a passing score of 675.The
exam covers a wide range of topics, including:
Hardware and Software
* Computer hardware components and their functions
- Operating systems and their functions
- Software applications and their uses
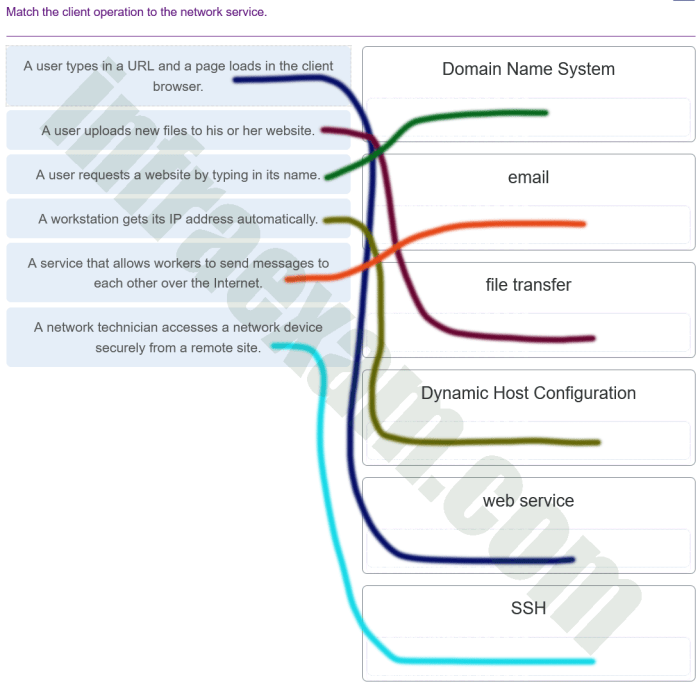
Networking
* Network topologies and protocols
- Network security
- Troubleshooting network issues
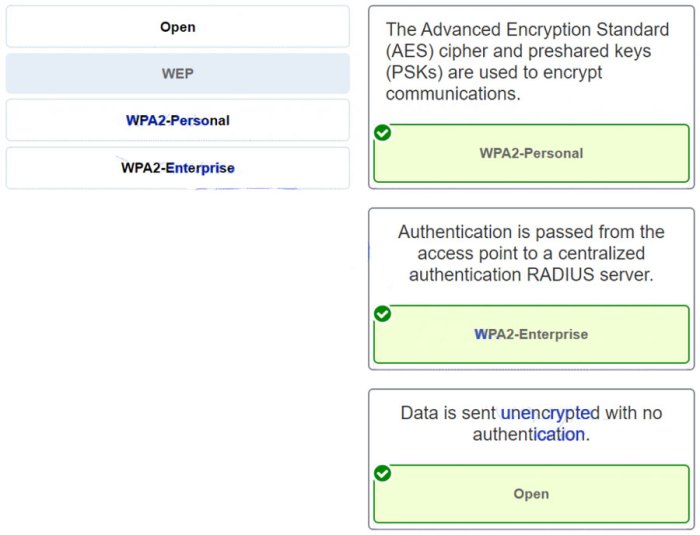
Security
* Security threats and vulnerabilities
- Security measures and best practices
- Disaster recovery and business continuity
Troubleshooting
* Troubleshooting methodologies
- Troubleshooting tools and techniques
- Troubleshooting common IT issues
Network Concepts
Networking fundamentals form the backbone of communication and data exchange in today’s digital world. Understanding these concepts is crucial for managing and troubleshooting networks effectively.
A network is an interconnected system of devices that can exchange information and share resources. It consists of various components, including computers, servers, switches, routers, and network interface cards (NICs), which facilitate communication between devices.
Network Types
Networks can be classified based on their size, purpose, and geographical coverage:
- Personal Area Network (PAN): Small-scale network connecting devices within a limited range, such as a home or office.
- Local Area Network (LAN): Network connecting devices within a single building or campus, providing high-speed data transfer.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): Network spanning a city or metropolitan area, connecting multiple LANs.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): Network covering a large geographical area, connecting devices across cities or countries.
- Global Area Network (GAN): Network spanning the entire globe, connecting devices worldwide.
Network Topologies
Network topology refers to the physical layout and arrangement of devices within a network. Common topologies include:
- Bus Topology: Devices are connected to a single shared cable, with signals transmitted in both directions.
- Ring Topology: Devices are connected in a closed loop, with signals traveling in one direction.
- Star Topology: Devices are connected to a central switch or hub, which manages data transmission.
- Mesh Topology: Devices are connected to multiple other devices, creating a redundant network.
- Hybrid Topology: A combination of two or more topologies, providing flexibility and redundancy.
Network Protocols, It essentials final exam 1-14
Network protocols define the rules and standards for communication between devices. Common protocols include:
- TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol): The primary protocol used for internet communication, providing reliable data transmission.
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): Used for transferring web pages and data between web browsers and servers.
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): Used for sending and receiving emails.
- DNS (Domain Name System): Translates domain names into IP addresses, facilitating internet navigation.
Hardware and Software
Computers consist of both physical components, known as hardware, and intangible components, known as software. Understanding the different types of hardware and software components is crucial for effective computer usage.
Hardware Components
Hardware components are the physical parts of a computer that can be touched and seen. They include:
- Processor (CPU): The “brain” of the computer, responsible for executing instructions and processing data.
- Memory (RAM): Stores data and instructions currently being processed by the CPU.
- Storage (HDD/SSD): Stores data permanently, even when the computer is turned off.
- Input Devices (Keyboard, Mouse): Allow users to interact with the computer.
- Output Devices (Monitor, Printer): Display information and print documents.
Software Components
Software components are the intangible instructions that tell the hardware what to do. They can be categorized into two main types:
- Operating Systems (OS): Manage the computer’s resources and provide a platform for running applications.
- Application Software: Specific programs designed to perform specific tasks, such as word processing, web browsing, or gaming.
Device Drivers
Device drivers are essential software components that allow the operating system to communicate with specific hardware devices. They ensure that the hardware functions properly and efficiently. Without device drivers, the operating system would not be able to recognize or use the hardware.
Security and Troubleshooting
Network security involves protecting networks and data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. Troubleshooting network issues is the process of identifying and resolving network problems to restore functionality and maintain network performance.
As you study for your IT Essentials final exam 1-14, you may encounter various topics. For instance, you might wonder, “What color tube is used for troponin?” To find the answer, you can refer to this article . Returning to your exam preparation, remember to thoroughly review all the key concepts to excel in your IT Essentials final exam 1-14.
Common Network Security Threats and Vulnerabilities
- Malware (viruses, worms, Trojans, spyware, ransomware)
- Phishing attacks
- Man-in-the-middle attacks
- DDoS (distributed denial of service) attacks
- Zero-day vulnerabilities
Network Troubleshooting
- Gather information (symptoms, error messages, recent changes)
- Test connectivity (ping, traceroute)
- Check hardware (cables, devices)
- Inspect software (updates, configurations)
- Analyze logs and traffic
- Implement solutions (patching, reconfiguration, isolation)
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
Benefits of cloud computing include:
- Cost savings: Cloud computing can help businesses save money on hardware, software, and IT staff.
- Scalability: Cloud computing can help businesses scale their IT resources up or down as needed.
- Flexibility: Cloud computing can help businesses be more flexible and responsive to changing needs.
- Reliability: Cloud computing can help businesses improve the reliability of their IT infrastructure.
- Security: Cloud computing can help businesses improve the security of their IT infrastructure.
Types of Cloud Services
There are three main types of cloud services:
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS provides access to software applications over the Internet.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS provides a platform for developing, deploying, and managing applications.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides access to the underlying infrastructure (e.g., servers, storage, and networks) that supports cloud computing.
Security Considerations for Cloud Computing
There are a number of security considerations that businesses need to be aware of when using cloud computing, including:
- Data security: Businesses need to ensure that their data is secure in the cloud.
- Access control: Businesses need to control who has access to their data and applications in the cloud.
- Compliance: Businesses need to ensure that their use of cloud computing complies with applicable laws and regulations.
Practice Questions
To reinforce your understanding of the exam topics, practice questions are essential. These questions will simulate the actual exam experience and help you identify areas where you need further review.
Below is a table with sample practice questions for each topic covered on the exam. Answer keys or explanations are provided to help you assess your progress.
Network Concepts
- What are the different types of network topologies and their advantages and disadvantages?
- Explain the difference between a LAN, WAN, and MAN.
- What is the purpose of a network protocol and what are the common protocols used?
Hardware and Software
- Identify the major components of a computer system and their functions.
- What is the difference between hardware and software?
- Explain the purpose of an operating system and its main functions.
Security and Troubleshooting
- What are the common types of network security threats and how to mitigate them?
- Explain the importance of regular system updates and patching.
- Describe the steps involved in troubleshooting network connectivity issues.
Cloud Computing
- What is cloud computing and what are its benefits?
- Explain the different types of cloud computing services.
- Discuss the security considerations for using cloud computing services.
Mock Exam
To simulate the actual exam experience, consider taking a mock exam. This will help you manage your time effectively, identify areas where you need additional preparation, and build confidence before the actual exam.
Exam Preparation Tips: It Essentials Final Exam 1-14
Effective Study Strategies
-
-*Create a study schedule
Break down the material into manageable chunks and set aside specific time slots for studying.
-*Active recall
Test yourself regularly by summarizing key concepts, answering practice questions, or teaching the material to someone else.
-*Spaced repetition
Review the material at increasing intervals to strengthen your memory.
-*Study groups
Join or form a study group to collaborate, discuss concepts, and quiz each other.
Time Management and Stress Reduction
-
-*Prioritize
Focus on understanding the most important concepts first.
-*Take breaks
Step away from studying regularly to clear your mind and return refreshed.
-*Manage stress
Exercise, meditate, or engage in other stress-reducing activities.
Additional Support
-
-*Online forums
Engage in discussions and ask questions on online forums dedicated to the exam.
-*Study groups
Connect with other students through university clubs, social media, or online platforms.
-*Practice exams
Take practice exams to simulate the actual exam and identify areas for improvement.
Popular Questions
What is the format of the IT Essentials Final Exam 1-14?
The exam consists of multiple-choice and true/false questions, covering topics such as networking, hardware, software, security, and cloud computing.
How much time is allotted for the exam?
You will have 90 minutes to complete the exam.
What is the passing score for the exam?
You need to score at least 70% to pass the exam.