Embark on a comprehensive journey through pharmacology with “Pharmacology HESI 55 Questions 2022,” an authoritative guide designed to equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to excel in your healthcare profession.
This meticulously crafted resource delves into the fundamental principles of pharmacology, empowering you to understand the mechanisms of drug action, metabolism, and excretion. Explore the intricacies of drug interactions, adverse reactions, and ethical considerations in pharmacological practice.
Pharmacology Concepts
Pharmacology is the study of drugs and their interactions with living organisms. It encompasses the understanding of drug properties, mechanisms of action, absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and therapeutic applications.
Fundamental principles of pharmacology include drug-receptor interactions, dose-response relationships, and pharmacokinetics. Different routes of drug administration, such as oral, intravenous, and transdermal, affect drug bioavailability and onset of action.
Commonly Used Drugs
- Acetaminophen: Analgesic and antipyretic
- Ibuprofen: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)
- Aspirin: Antiplatelet and anti-inflammatory
- Warfarin: Anticoagulant
- Metformin: Antidiabetic
Drug Metabolism and Excretion
Drug metabolism involves the chemical transformation of drugs in the body, primarily in the liver. Metabolites can be more or less active than the parent drug.
Excretion is the process by which drugs and their metabolites are eliminated from the body, mainly through the kidneys (urine) and feces.
Metabolic Pathways
- Phase I: Oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis
- Phase II: Conjugation with glucuronic acid, sulfate, or glutathione
Examples
- Paracetamol: Metabolized to inactive metabolites
- Morphine: Metabolized to active metabolite morphine-6-glucuronide
Drug Interactions

Drug interactions occur when two or more drugs are taken together and affect each other’s efficacy or safety.
Types of Interactions
- Pharmacokinetic: Alteration of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, or excretion
- Pharmacodynamic: Modification of drug effects at the target site
Consequences
- Increased or decreased drug efficacy
- Increased toxicity
- Therapeutic failure
Management Strategies
- Avoid combining interacting drugs
- Adjust drug doses or administration times
- Monitor for adverse effects
Adverse Drug Reactions
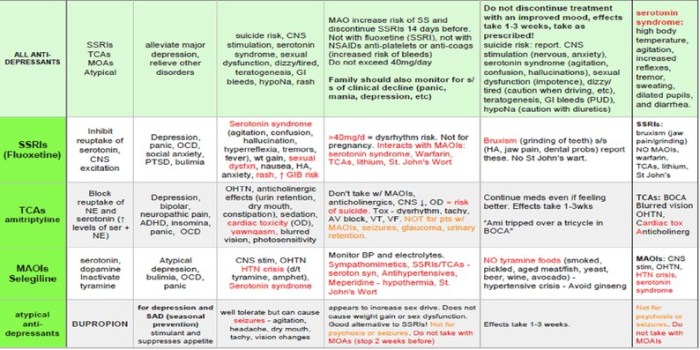
Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) are unintended and harmful effects of drugs.
Types of ADRs
- Type A: Predictable, dose-related
- Type B: Unpredictable, non-dose-related
- Type C: Long-term use
- Type D: Delayed onset
Risk Factors
- Age
- Genetic factors
- Drug interactions
- Polypharmacy
Prevention and Management
- Careful drug selection and dosing
- Patient education and monitoring
- Reporting and analysis of ADRs
Pharmacotherapy for Common Conditions
Pharmacotherapy involves the use of drugs to treat and manage various medical conditions.
Cardiovascular Disease
- Antihypertensives: Lower blood pressure
- Antianginals: Relieve chest pain
- Anticoagulants: Prevent blood clots
Diabetes
- Insulin: Regulates blood sugar levels
- Oral hypoglycemics: Lower blood sugar levels
Pain Management
- Analgesics: Relieve pain
- Opioids: Strong pain relievers
- Non-opioid pain relievers: Acetaminophen, NSAIDs
Clinical Pharmacology

Clinical pharmacology evaluates the safety and efficacy of drugs in humans.
Drug Development and Evaluation
- Preclinical studies: Animal testing
- Phase I trials: Safety and dosage in healthy volunteers
- Phase II trials: Efficacy and safety in patients
- Phase III trials: Large-scale trials to confirm efficacy and safety
Examples of Clinical Pharmacology Studies
- Statin trials: Lowering cholesterol levels to prevent cardiovascular disease
- Antidepressant trials: Evaluating the efficacy of new antidepressants
Ethical Considerations in Pharmacology
Ethical principles guide the use and development of drugs.
Informed Consent, Pharmacology hesi 55 questions 2022
Patients must fully understand the risks and benefits of drug therapy before consenting to treatment.
Patient Autonomy
Patients have the right to make decisions about their own healthcare, including drug use.
Ethical Dilemmas
- Placebo use in clinical trials
- Off-label drug use
- Drug addiction and abuse
FAQ Insights: Pharmacology Hesi 55 Questions 2022
What are the key principles of pharmacology?
Pharmacology encompasses the study of drug actions, interactions, and effects on living organisms, including humans.
How do drugs enter the body?
Drugs can enter the body through various routes, including oral, intravenous, topical, and inhalation.
What factors influence drug metabolism?
Drug metabolism is influenced by factors such as age, genetics, liver function, and drug interactions.
What are the potential consequences of drug interactions?
Drug interactions can alter drug efficacy, increase toxicity, or lead to adverse reactions.
How can adverse drug reactions be prevented?
Preventing adverse drug reactions involves careful patient assessment, appropriate drug selection, and monitoring for potential interactions.