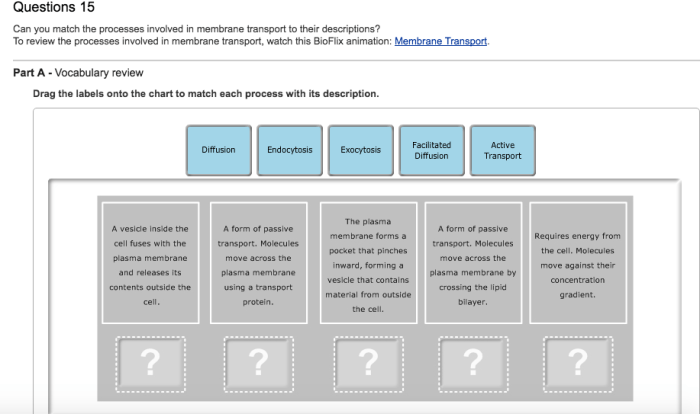
Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of cell transport with our comprehensive guide to the Cell Transport Concept Map Worksheet Answers. This meticulously crafted resource unveils the intricate mechanisms that govern the movement of substances across cell membranes, shaping the very essence of life.
Our comprehensive guide delves into the diverse array of cell transport mechanisms, providing illuminating examples and highlighting their profound significance in maintaining cellular homeostasis. Prepare to unravel the intricate tapestry of cell transport as we navigate through this educational odyssey.
Cell Transport Mechanisms
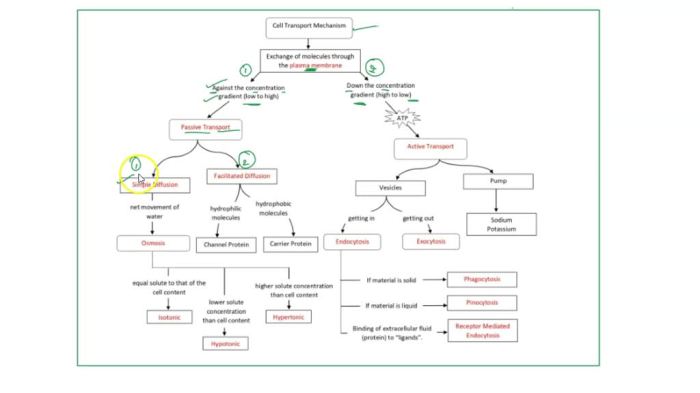
Cell transport mechanisms are essential for the proper functioning of all living organisms. They allow cells to exchange nutrients, waste products, and other molecules with their surroundings. There are two main types of cell transport mechanisms: passive transport and active transport.
Passive Transport
- Does not require energy.
- Molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
- Examples: diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion.
Active Transport
- Requires energy (ATP).
- Molecules move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration.
- Examples: ion pumps, endocytosis, and exocytosis.
Importance of Cell Transport Mechanisms, Cell transport concept map worksheet answers
Cell transport mechanisms are essential for the following:
- Maintaining homeostasis within cells.
- Acquiring nutrients for cellular processes.
- Removing waste products from cells.
- Communicating with other cells.
Cell Transport Concept Map
The following concept map illustrates the different types of cell transport mechanisms:
- Cell Transport Mechanisms
- Passive Transport
- Diffusion
- Osmosis
- Facilitated Diffusion
- Active Transport
- Ion Pumps
- Endocytosis
- Exocytosis
Worksheet Answers: Cell Transport Concept Map Worksheet Answers
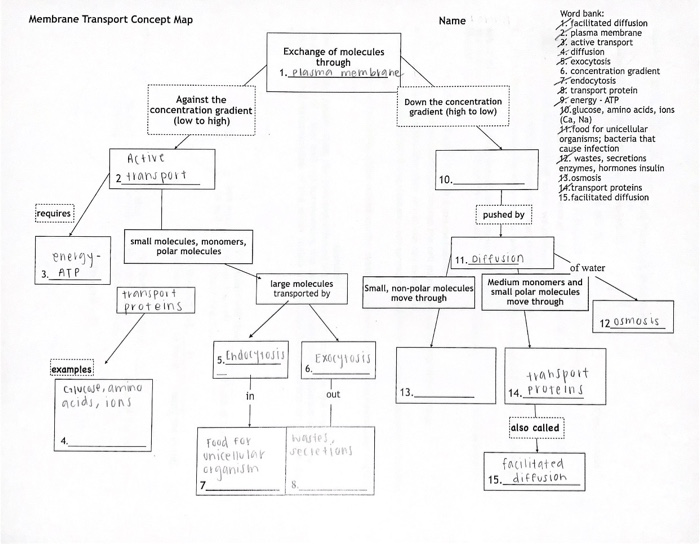
1. What are the two main types of cell transport mechanisms?
Passive transport and active transport.
2. Which type of cell transport mechanism does not require energy?
Passive transport.
3. Give an example of an active transport mechanism.
Ion pumps.
4. What is the importance of cell transport mechanisms?
Cell transport mechanisms are essential for maintaining homeostasis within cells, acquiring nutrients for cellular processes, removing waste products from cells, and communicating with other cells.
Top FAQs
What are the primary types of cell transport mechanisms?
Cell transport mechanisms can be broadly classified into two main categories: passive transport and active transport.
What is the significance of cell transport mechanisms?
Cell transport mechanisms play a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, facilitating the exchange of nutrients, waste products, and signaling molecules across cell membranes.
How can the Cell Transport Concept Map Worksheet Answers enhance my understanding of cell transport?
The Cell Transport Concept Map Worksheet Answers provide a structured and visually engaging representation of the different cell transport mechanisms, aiding in the comprehension and retention of complex biological concepts.