Cumulative flow diagram focuses on which curves – Cumulative flow diagrams (CFDs) stand as indispensable tools in project management, offering a visual representation of project progress and workflow. By focusing on key curves, CFDs provide valuable insights into project performance, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement.
CFDs depict the movement of work through a project’s stages, allowing project managers to track the amount of work in progress, lead time, cycle time, and cumulative flow. These curves provide a comprehensive view of project progress, helping teams identify inefficiencies and make informed decisions.
Cumulative Flow Diagrams: A Tool for Visualizing Project Flow
Cumulative flow diagrams (CFDs) are graphical representations that visualize the flow of work through a project over time. They provide insights into the progress of the project, identify bottlenecks, and help teams improve their workflow.
Types of Curves in a CFD
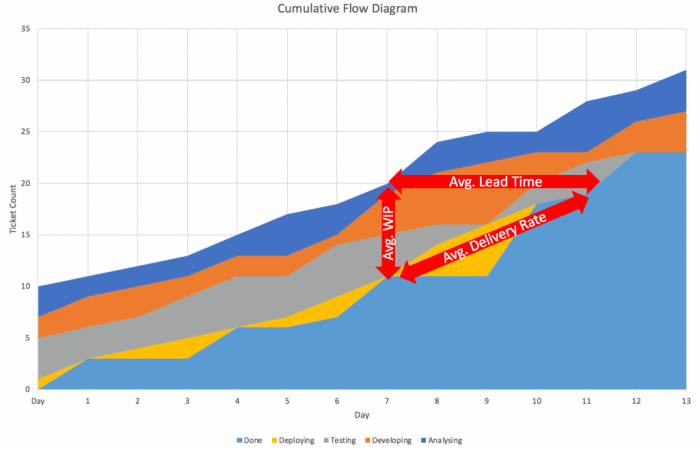
- Work in Progress (WIP) Curve:Represents the amount of work in progress at any given time.
- Lead Time Curve:Measures the time it takes for work to flow from start to completion.
- Cycle Time Curve:Represents the time it takes for a single unit of work to move through the system.
- Cumulative Flow Curve:Provides a comprehensive view of project progress by accumulating the WIP over time.
Work in Progress (WIP) Curve
The WIP curve indicates the amount of work that is currently being worked on. A high WIP curve may indicate that the team is taking on too much work or that the workflow is inefficient.
Lead Time Curve
Lead time is the time it takes for work to flow from start to completion. A long lead time may indicate bottlenecks or inefficiencies in the workflow.
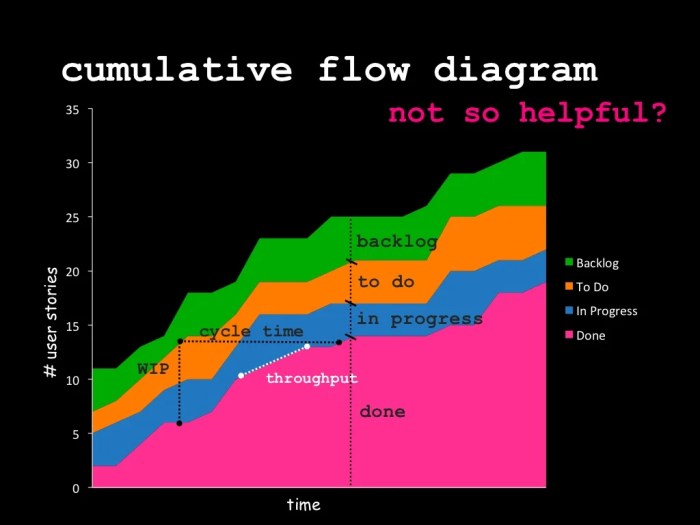
Cycle Time Curve
Cycle time is the time it takes for a single unit of work to move through the system. A long cycle time may indicate that the team is not working efficiently or that there are bottlenecks in the workflow.
Cumulative Flow Curve
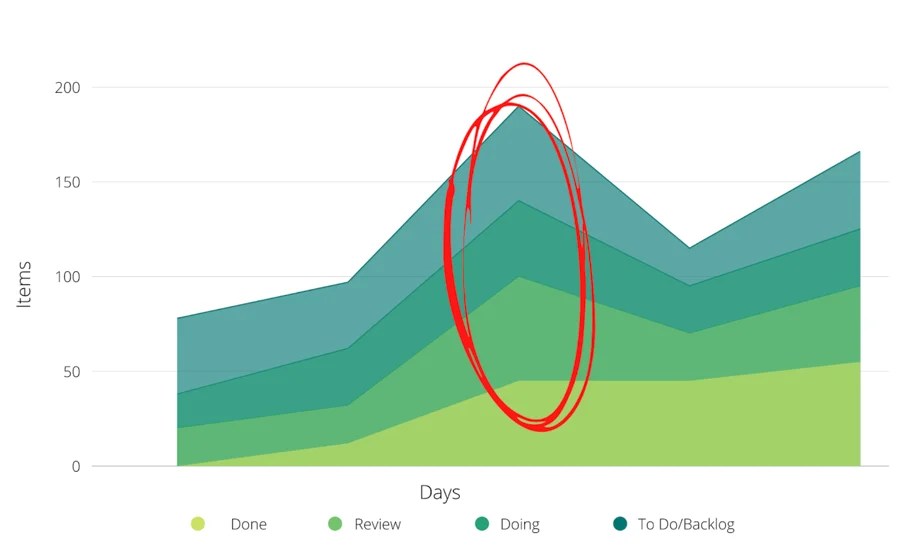
The cumulative flow curve provides a comprehensive view of project progress by accumulating the WIP over time. It can be used to identify trends and patterns in the workflow.
Using CFDs to Analyze Project Performance, Cumulative flow diagram focuses on which curves
- Identify bottlenecks:CFDs can help identify areas in the workflow that are causing delays.
- Monitor progress:CFDs provide a visual representation of project progress, making it easy to track progress and identify any potential issues.
- Improve workflow:By understanding the flow of work, teams can identify areas for improvement and make changes to improve efficiency.
Limitations of CFDs
- Complexity:CFDs can be complex to interpret, especially for large projects with multiple workflows.
- Data accuracy:The accuracy of CFDs depends on the accuracy of the data that is used to create them.
- Subjectivity:CFDs can be subjective, as they are based on the interpretation of the data.
FAQ Section: Cumulative Flow Diagram Focuses On Which Curves
What is the purpose of a cumulative flow diagram?
CFDs provide a visual representation of project progress, allowing teams to track work in progress, lead time, cycle time, and cumulative flow.
What are the different types of curves displayed on a CFD?
CFDs typically display WIP, lead time, cycle time, and cumulative flow curves.
How can CFDs be used to identify bottlenecks?
By analyzing the cycle time curve, project managers can identify stages in the workflow that are causing delays and bottlenecks.