Simulation lab 6.2: module 06 understanding the rsa encryption system – Embark on a journey into the world of cryptography with Simulation Lab 6.2, Module 06: Understanding the RSA Encryption System. This comprehensive guide unveils the intricate workings of RSA, a cornerstone of modern cryptography, exploring its mathematical foundations, applications, and security considerations.
Delve into the minds of the brilliant individuals who shaped RSA, unraveling the mathematical principles that underpin its strength. Witness the step-by-step process of RSA encryption and decryption, unraveling the secrets of secure communication and digital signatures.
RSA Encryption System Overview: Simulation Lab 6.2: Module 06 Understanding The Rsa Encryption System
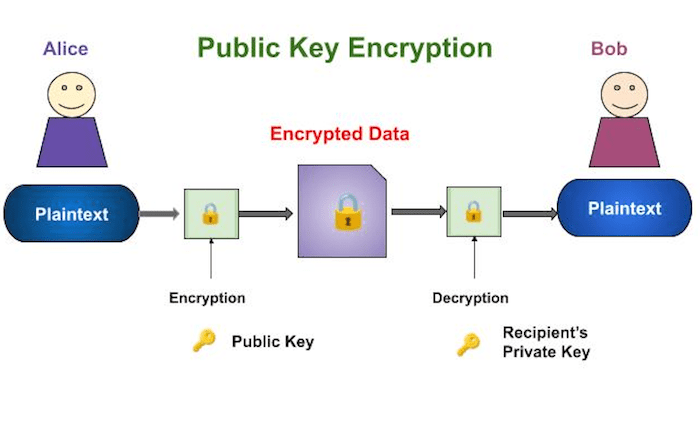
RSA, named after its inventors Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman, is a widely used public-key encryption algorithm that provides secure communication over insecure channels. It relies on the mathematical difficulty of factoring large numbers and has revolutionized the field of cryptography.
RSA Algorithm: Mathematical Foundations, Simulation lab 6.2: module 06 understanding the rsa encryption system
RSA is based on modular arithmetic and the concept of trapdoor functions. It involves generating two large prime numbers, p and q, and computing their product n. The public key consists of n and a publicly known encryption exponent e, while the private key consists of the decryption exponent d.
The security of RSA stems from the difficulty of finding d given n and e.
RSA Encryption and Decryption Process
Encryption involves converting a plaintext message M into ciphertext C using the public key (n, e): C = M^e mod n. Decryption requires the private key (n, d): M = C^d mod n. The mathematical properties of RSA ensure that only the holder of the private key can decrypt the ciphertext.
RSA Applications and Use Cases
RSA finds applications in secure communication, digital signatures, and blockchain technology. It enables secure data transmission, authentication, and the creation of digital certificates. RSA is widely used in industries such as finance, healthcare, and government for protecting sensitive information.
Security Considerations and Cryptanalysis
RSA is vulnerable to brute-force attacks and side-channel attacks. However, large key sizes and ongoing research in cryptanalysis techniques mitigate these vulnerabilities. Advances in quantum computing pose potential threats to RSA, leading to the development of quantum-resistant encryption algorithms.
Comparison with Other Encryption Algorithms
RSA is compared to AES and ElGamal encryption algorithms. While RSA excels in public-key encryption, AES is more efficient for symmetric encryption. ElGamal provides similar security but requires larger key sizes. The choice of algorithm depends on the specific application requirements.
Future of RSA and Quantum Computing
Quantum computing poses challenges to RSA’s security. Quantum-resistant encryption algorithms, such as Lattice-based cryptography and McEliece encryption, are being developed to address these threats. The future of RSA will depend on advancements in quantum computing and the development of new encryption techniques.
Common Queries
What is the significance of RSA in modern cryptography?
RSA is a cornerstone of modern cryptography due to its ability to provide both confidentiality and authenticity in secure communication. It underpins digital signatures, secure messaging, and blockchain technology, ensuring the integrity and privacy of sensitive data.
How does the mathematical foundation of RSA contribute to its security?
RSA’s security relies on the mathematical difficulty of factoring large prime numbers. The mathematical principles underlying RSA, such as modular arithmetic and prime factorization, make it computationally infeasible to break the encryption without the private key.
What are the potential vulnerabilities associated with RSA?
RSA is vulnerable to brute-force attacks, where attackers attempt to guess the private key through exhaustive trial and error. Side-channel attacks, which exploit physical characteristics of the system, can also compromise RSA’s security. Ongoing research focuses on mitigating these vulnerabilities and enhancing the security of RSA.